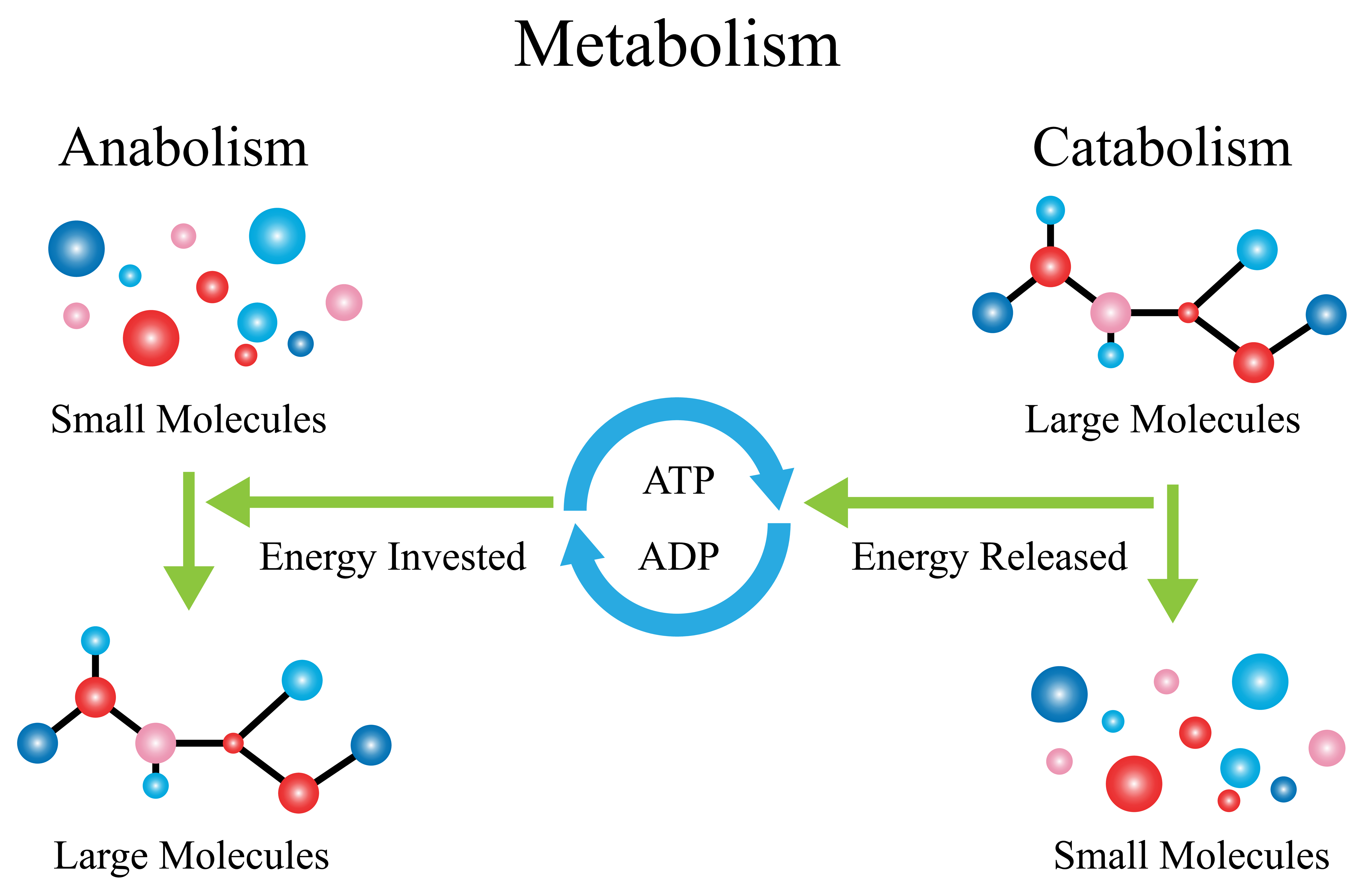
Metabolism refers to the collection of chemical reactions that occur within living organisms. It consists of two main processes: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism breaks down large molecules into smaller ones to release energy. Anabolism builds larger molecules from smaller ones, consuming energy in the process.
Not all metabolic processes happen in every cell. Instead, cells must adjust the rate at which molecules move through these pathways to function efficiently. Metabolic pathways typically involve some reversible reactions under normal conditions and a few that are irreversible.
Fats provide energy through fatty acid β-oxidation, followed by the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Carbohydrates are broken down via glycogen or starch degradation and glycolysis, also followed by the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Proteins are broken down into amino acids. These contribute to energy metabolism by entering glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
After eating, energy becomes readily available. When blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin, which promotes the uptake of glucose into various tissues such as the liver and muscles. This leads to the storage of energy as glycogen and triacylglycerols, while protein synthesis and other biosynthetic pathways are enhanced.
As you age, metabolism typically slows down for several reasons, including muscle loss and reduced physical activity. However, there are effective ways to boost your metabolism, such as getting adequate sleep, drinking tea, and consuming sufficient protein and calories.
The Boom Health app allows users to book registered nurses, personal support workers, and personal care services, schedule transportation, order prepared meals, rent or purchase medical equipment, and get emergency assistance. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.