Inflammation plays a role in the body’s healing process, however, it is also a significant risk factor for numerous health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and certain cancers. When inflammation happens, your body is protected from substances including infections and microbes by chemicals in white blood cells that enter the blood or tissues. This causes redness and warmth because there is increased blood flow to that area. Here’s where the anti-inflammatory diet comes into play.
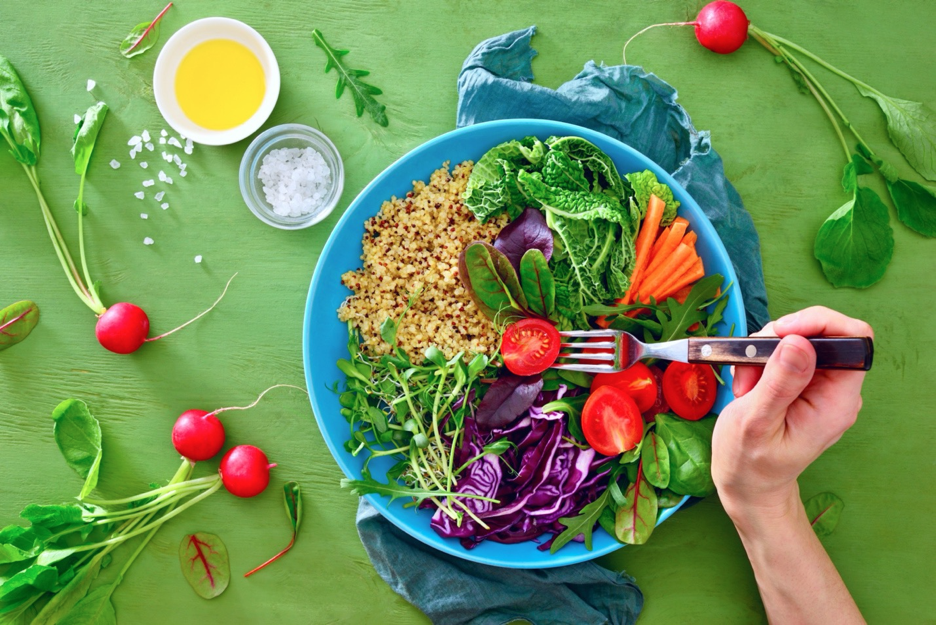
The anti-inflammatory diet encourages the consumption of fatty fish such as salmon and tuna because they are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation. Fruits and vegetables with lots of colour, nuts, and beans are also encouraged. Nuts have healthy fats that prevent inflammation, but it is recommended to not consume more than a handful of nuts per day because they are high in calories and fat. Beans are high in fiber, anti-inflammatory substances, and antioxidants, which prevent or slow damage to cells.
Certain foods such as processed meats, refined carbohydrates, and foods with trans fats can increase inflammation, and therefore, it is recommended to limit the intake of these foods.
There are many benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet. Some include an improvement in mood and energy, decreased risk of depression, and better blood sugar levels.
To maintain an anti-inflammatory diet, consider trying meal prep. This will make it easier for you to eat healthy during the next week if you have a plan in place. Also, prepare a shopping list before going to the grocery store so you will be less tempted to purchase convenience foods. Finally, drink lots of water, to help regulate body temperature, prevent infections, and keep organs functioning properly.
The Boom Health app allows you to book and manage all your in-home care needs. Helping families care for their loved ones at home is at the centre of Boom’s vision and mission. Find the app on the App Store or Google Play Store today.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.