Inflammation is a response of vascularized tissues (contain vessels) that delivers leukocytes (white blood cells) and molecules of host defense from the circulation to the sites of infection and cell damage in order to eliminate the offending agents.
It can be classified as acute or chronic depending on how long it lasts. Pain or tenderness, heat, and swelling may be caused by acute inflammation, which typically lasts for only a few hours or days. In contrast, signs of chronic inflammation may include fatigue, fever, and skin rash. This condition can last for months or even years.
There is an association between inflammation and several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Huntington’s disease.
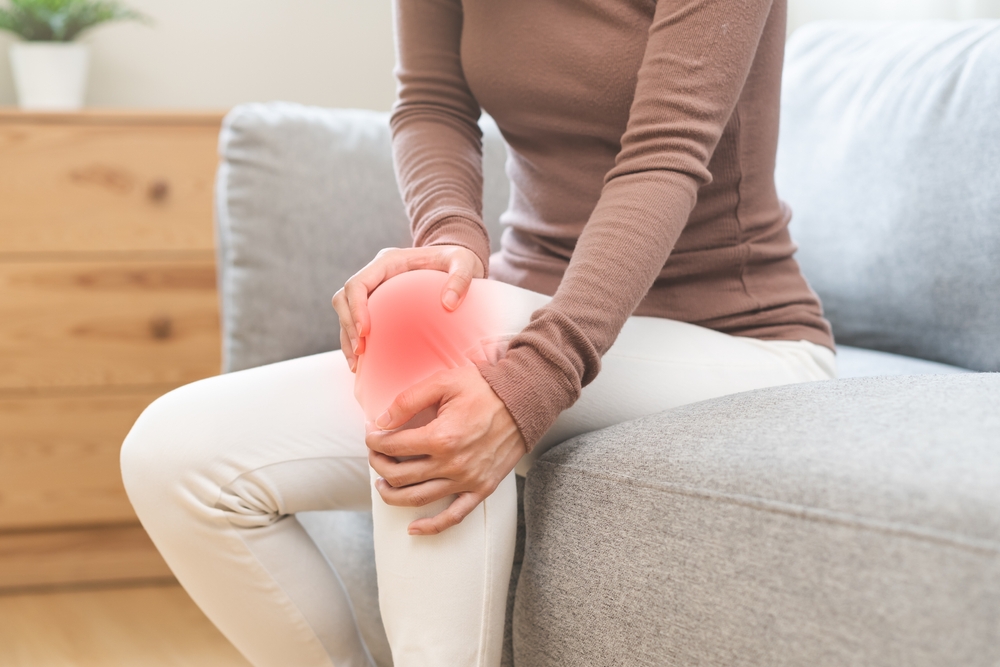
Many types of arthritis, including gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, are caused by inflammation.
The inflammatory response begins when injured tissue cells release chemical signals that activate cells lining capillaries (blood vessels). Mast cells degranulate and release histamine, which causes vasodilation (expansion), allowing neutrophils (white blood cells) to enter the tissue fluid. Neutrophils ingest and destroy invading bacteria.
To prevent inflammation, try to limit your alcohol consumption, remain physically active, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid smoking.
Inflammation can be treated through the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroid injections, and supplements. In addition to reducing inflammation, NSAIDs prevent blood clots, decrease fever, and reduce pain.
Love them without losing yourself. The Boom Health app helps you manage your loved one’s home care in one app. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.