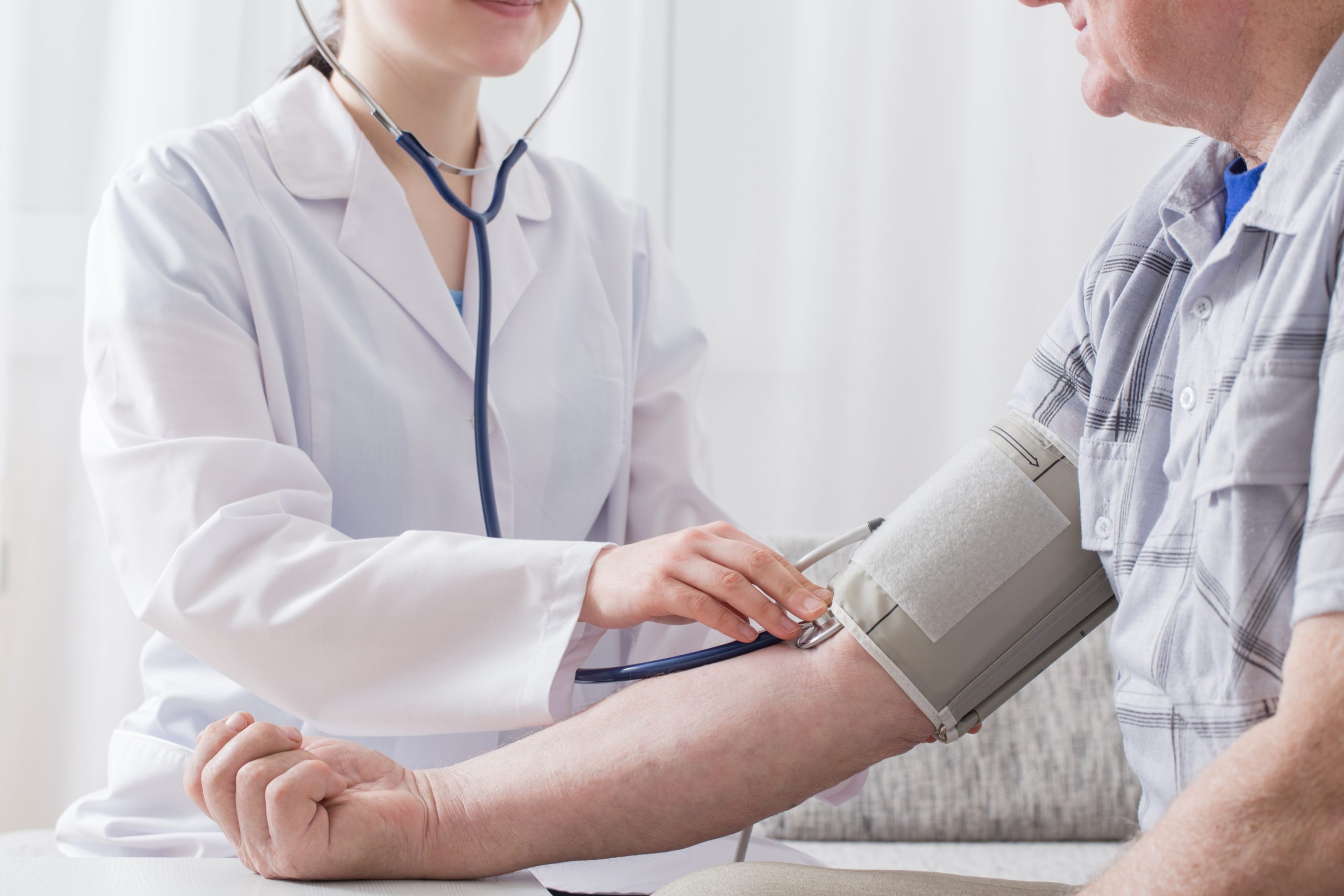
Hypertension is defined as elevated blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps blood throughout the body. The two phases of the cardiac cycle are systole and diastole. Systole is when the heart contracts and pumps blood out of the heart. Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills after a contraction.
Blood pressure classification
Normal blood pressure is classified as systolic blood pressure less than 120 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure less than 80 mmHg. Prehypertension is diagnosed if a patient’s systolic blood pressure is 120–139 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure is 80–89 mmHg. A stage 1 hypertension classification is made if the systolic blood pressure ranges from 140 to 159 mmHg or the diastolic blood pressure ranges from 90 to 99 mmHg. Finally, stage 2 hypertension is diagnosed if a patient has a systolic blood pressure greater than 160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 100 mmHg.
Primary and secondary hypertension
Approximately 92% of hypertension cases are primary hypertension, which has no cause. On the other hand, secondary hypertension has many causes including kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, sleep apnea, and oral contraceptive use.
The condition of your kidneys and the levels of certain hormones in your body can influence blood pressure. In addition, obesity, stress, smoking, a high salt diet, and diabetes are risk factors for developing hypertension.
There is an association between chronic hypertension and morbidity and mortality. Untreated hypertension can cause heart attacks, kidney failure, strokes, and retinal damage.
Effective lifestyle changes to help maintain a normal blood pressure are decreasing body weight, restricting sodium intake, and quitting smoking.
The Boom Health app allows you to find caregivers, book personal services, order prepared meals, rent or purchase medical equipment, get emergency assistance, and schedule transportation. Download the app on the App Store or Google Play Store to get started.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.